Machine manufacturing enterprises use a lot of high-capacity production machines. Therefore, the power supply system of an industrial enterprise requires a large load capacity, stable and continuous supply to ensure the smoothest and most efficient operation. So what are the characteristics of the electrical system in these enterprises, let’s follow through the following article.
1. Technological characteristics of machine-manufacturing industrial enterprises
Machine manufacturing industry is one of the industries with strong development potential in recent years.
With the nature of a heavy industry, the industrial machine building requires a large number of modern machines and production lines. Therefore, the power supply system of the industrial enterprise must also have strong performance, ensuring sufficient power supply for the production activities of the enterprise.
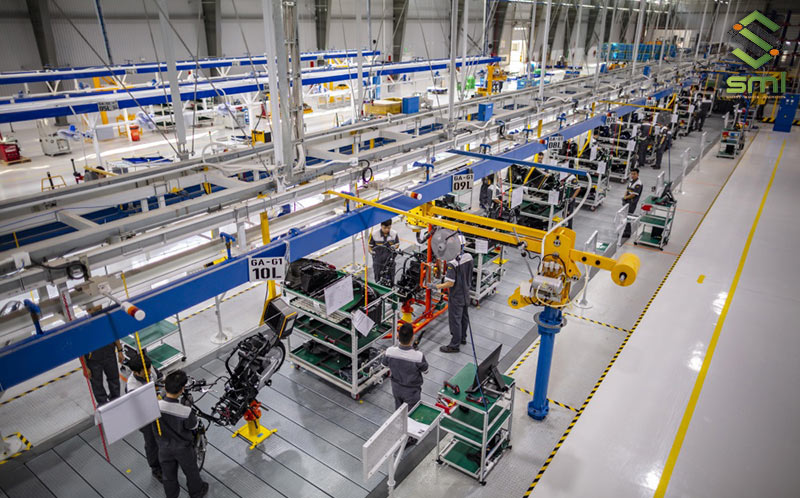

The technological line has the following characteristics:
- Stage 1: Making embryos:
Different types of metals such as cast iron, steel, copper, aluminum, etc. will be selected in appropriate proportions and cooked to form ingots.
The billet is usually smelted in specialized smelters in production. Enterprises often integrate crane systems to pour molten metal into casting molds or move workpieces after smelting.
- Stage 2: Forging and trimming the billet
After cooking, the workpiece will be transferred to hydraulic compressor systems, large capacity forging and stamping machines, etc. to create preliminary shapes. Then continue to be cleaned and trimmed the excess parts such as joints, bavia, … And finally will be welded and cut into blocks according to the given shape and size.
- Stage 3: Machining machine parts
The preforms are transferred to the next workshop to be processed into machine parts. This process uses many different types of machines and equipment such as lathes, planers, grinders, drills, mills, reamers, valves, etc. with many different sizes and capacities. They can be organized as an automatic line or used separately depending on the characteristics of each factory.
This is the most important stage as well as the stage that uses the most machines and equipment in the entire production process of the machine-manufacturing enterprise.
- Stage 4: Heat treatment
Machine parts operating in harsh environments or frequently subjected to friction such as gears, shafts, etc. will be heat treated to increase durability.
Here, businesses often use furnaces, furnaces, high-rise furnaces, etc. and other specialized furnaces to process heat for machine parts.
- Stage 5: Final processing
Machine parts will continue to be final processed to ensure compliance with the applicable manufacturing standards
- Stage 6: Assemble into complete machine
After the machine parts have met the necessary standards, they will be put on the automatic assembly line to create a complete machine.
This production line works in an automatic way. Any failure on the system will cause downtime and can not continue to produce products. Therefore, the demand for stable and continuous power supply is also higher than that of other separately operated machine systems.
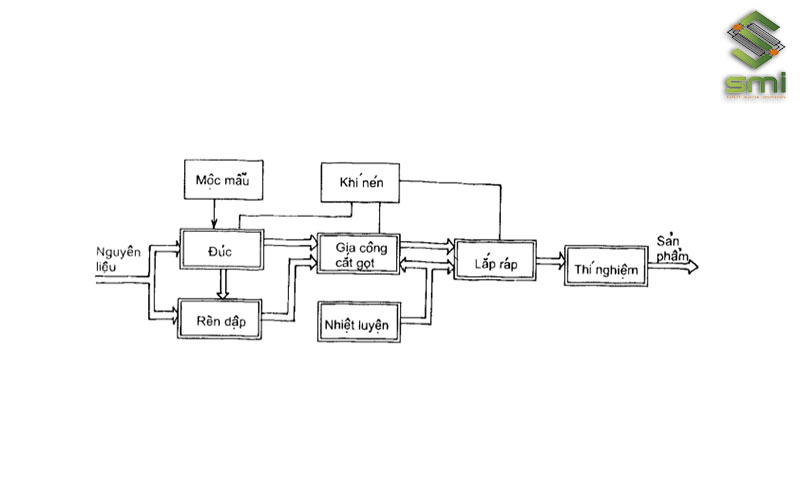
Machine manufacturing is one of the industries that concentrates a large amount of machinery and has many different processing stages. Therefore, for smooth and efficient production activities, enterprises need an efficient power system, careful calculation of electrical loads, equipment, and power sources, ensuring stable and continuous supply of power. necessary capacity.
2. Electrical load for machine-manufacturing industrial enterprises
Electrical load is a quantity measured by the total power consumed by the entire system of equipment using electricity at a time. This is one of the important factors to determine when designing and operating industrial electrical systems.
An efficient electrical system is when it provides a balance between the estimated electrical load and the actual total consumption. If this is not guaranteed, two problems arise:
- Estimated electrical load is smaller than actual : Machines and equipment that are not supplied with enough power will not operate at their correct capacity, leading to inefficiency in production. In addition, operating under a weak power source can also cause damage and reduce the life of the machinery system.
- Estimated electrical load is larger than actual : An electrical load that is much larger than the actual load will cause waste because the power system cannot consume all the inherent energy.
Enterprises now often classify electrical loads into 3 types:
- The equipment and machines work in automatic lines
Automated production line systems create a continuous and synchronous operation in the production process. The power supply for the automatic line system must be strong and stable enough. Any failure on one device affects the operation of the entire line.
- Equipment and machines working on non-automatic lines
The production line system does not automatically produce products through many different stages, sequentially but not continuously. This can be understood that: An industrial steel pipe must be produced through many stages such as ingot cooking, casting, forging, quenching, plating, etc. All stages need to be performed on many machines, execute sequentially in the order of the process.
Problems on one machine affect only that machine, not the entire line. Other jobs can be continued. Damaged machines can be re-entered into production after being repaired or replaced.
- Individual working machines and equipment
The machines are used for unrelated jobs. An issue that occurs on one machine affects only the machine itself.
The electrical load at the factory needs to be balanced when operating production. Enterprises should avoid starting up large-capacity production machinery and equipment at the same time to reduce pressure on the electrical system, minimize the risk of overload, fire or short circuit, etc.
3. Power supply system at machine-manufacturing industrial enterprises
3.1. Current and voltage
Electricity used in industrial production has a much higher voltage than the power source for civil needs.
The supply voltage for factories and production workshops is the medium and high voltage power network
U = 10 – 22kV, up to 35 – 110kV if “deep conduction” of the power network. Businesses will have to lower the power supply voltage to 380/220 V before putting it into use. In some special cases, the power used may be as low as 36V.
Factories and industrial workshops often use AC power with a frequency of 50Hz. Some businesses use the inverter method to adjust the speed of machine systems using AC drives. Common variable frequency levels are usually in the range f = 10 – 50Hz, or f = 50 – 300 Hz. For high-frequency heaters, it is common to use inverters with a value of f = 10000 Hz.
3.2. Power distribution network of the enterprise
The electricity network used at the enterprise is produced and distributed by EVN. Large-scale enterprises often use electricity from regional sources (35 – 110 kV). Meanwhile, small-scale enterprises often choose to use electricity supplied from distribution stations in the city (10-22 kV).
The power supply station will divide the flow and conduct electricity to the transformer stations of factories and enterprises through the transmission line.
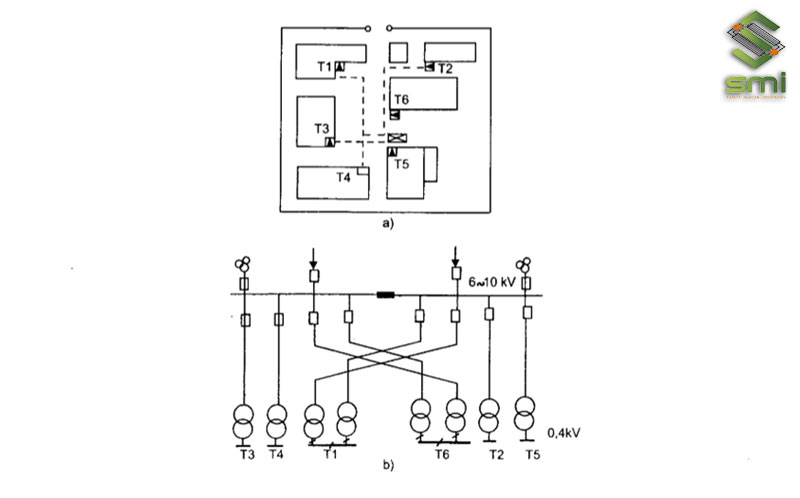
The power distribution station can simultaneously provide two power transmission lines to the enterprise. Enterprises usually only use one wire, the other line is used as a backup in case the main line has a problem.
The distribution network of factories and enterprises should use cables, both to ensure safety and to create beauty for businesses. For small enterprises or temporary construction department, it is possible to go electric by overhead line to optimize the source of costs.
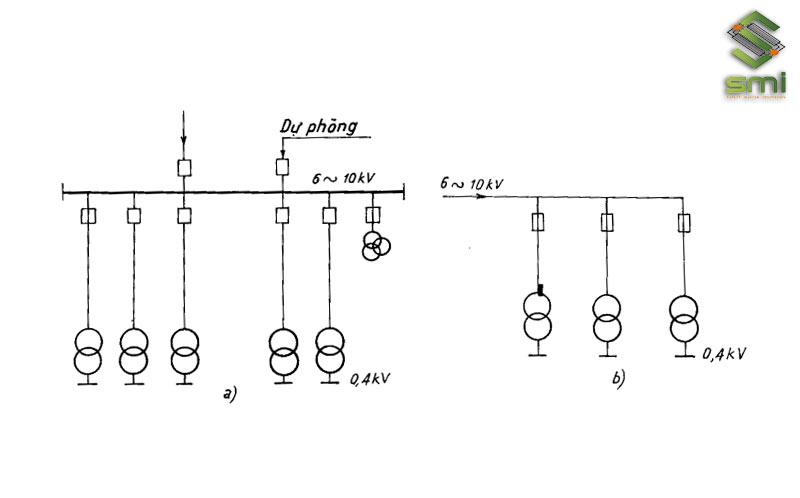
Normally, enterprises have to build intermediate substations to convert power from 22 – 110kV to the appropriate voltage level.
In order to make the diagram of the power supply system of an industrial enterprise simpler and more flexible, the enterprise should arrange more distribution stations to ensure a stable power source for the operation of electrical equipment. According to the experience of many people, installing a distribution station for 3000 – 5000 kVA of electrical load is appropriate.
3.3. Factory electrical network
Factories and enterprises in many different fields have different working environments and electrical load characteristics. Therefore, the structure and method of distribution and installation of the distribution network in each enterprise are also very different.
Workshops with large electrical loads and relatively even distribution of equipment and machinery such as workshops for processing, welding, forging, stamping, assembly, etc. usually distribute the electrical network according to the transformer diagram – spindle wire (figure a).
Workshops do not have many equipment, but each machine has a very large operating capacity such as smelting furnaces, smelters, forgings, steel tempering, arc furnaces, etc. Enterprises often use shaped distribution networks. rays for power supply (Figure b).
Workshops play other auxiliary roles of factories and enterprises such as lighting zones, carpentry workshops, warehouses, etc., just need to arrange a branched electrical network (Figure c).
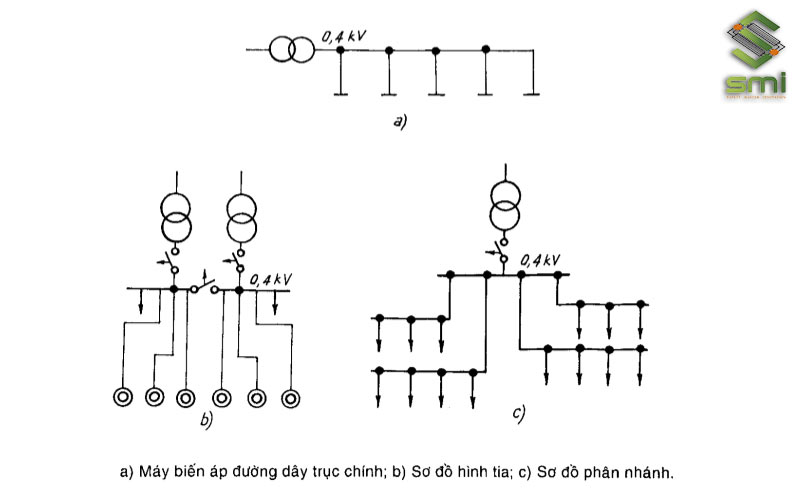
In order to ensure that the factory electrical network can operate smoothly, businesses also arrange to install additional auxiliary substations and apply automatic reserve closing methods.
In addition, the issues of fire prevention, ventilation, … all need to be paid attention to comply with the state’s regulations on electrical safety in industrial production.
3.4. Lighting in machinery manufacturing industry
Lighting has a direct impact on production efficiency, worker health and safety. Therefore, when arranging lighting at a machine-building factory, the constructor needs to carefully study the specific characteristics of the factory to conduct appropriate installation.
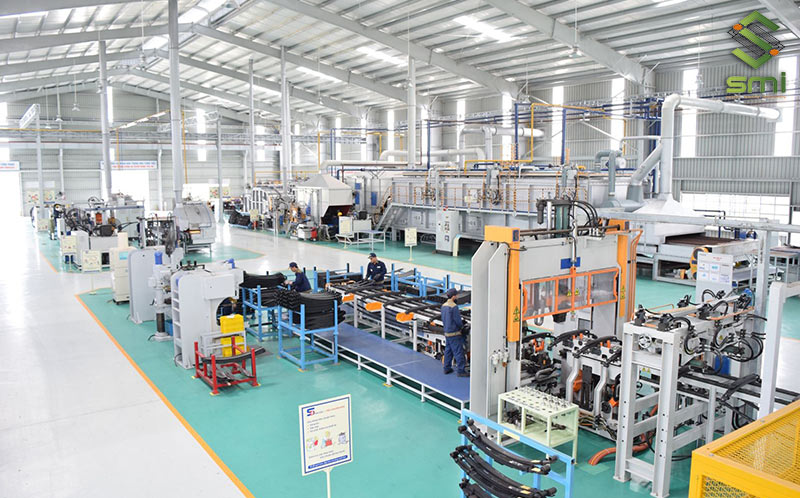

Some notes when installing lighting in the workshops of machine-building enterprises are as follows:
- The cutting and trimming workshop is characterized by a fairly uniform distribution of equipment and machinery on the ground. Therefore, the lighting system is usually arranged evenly with the necessary illuminance from 30 – 50 lx;
- The workshop has high-capacity machines, large size causing many dark patches that will make the workshop space dark. At this time, the lighting system will be arranged in a selectively distributed manner to ensure brightness where needed. In addition, the processing parts need to be equipped with a local lighting system using 36 V source, 150 – 1000 lx illuminance to serve the lighting needs when working.
- The assembly workshop can carry out work across the production site. The general lighting is evenly distributed with a guaranteed illuminance of 50 – 75 lx. In addition, assembly workers also need to be provided with auxiliary lights to increase lighting in the workplace. These lamps are usually portable portable lights that use 24 or 36 V power;
- Cold workshops need to install the general lighting system and local lighting at the cold tables at the same time;
- The carpentry workshop should use a type of light with a protective cover to limit dust and the risk of fire and explosion;
- The foundry should use dust-proof lights. In addition, for the mold making part, workers need to be equipped with mobile lights to make it easier to check mold quality;
- Hot processing workshops and high-risk workshops should be equipped with emergency lighting systems to help employees evacuate easily in case of power outages or production problems;
- Other workshops such as compressed air station, pumping station, outdoor lighting, etc. are installed with basic lighting because there is nothing special.
4. Some solutions to save electricity for the electrical system of the machine building industry
There are many solutions to help save electricity for the power supply system of industrial machinery manufacturing enterprises. They are carried out simultaneously even during the design and operation of the power system.
4.1 Design phase
This phase includes four stages as follows:
- Step 1: Choose the power supply diagram
The arrangement of the electrical network according to the appropriate distribution diagram will help to provide enough power for the entire system of production machinery and equipment, and at the same time ensure the safety of the electrical system, and minimize the occurrence of incidents in the system. the process of loading and using electricity in production.
Noteworthy issues include: choosing voltage level, choosing transformer capacitance in accordance with actual load, conductor cross-section, distribution station distribution, reasonable load and wiring, etc.
- Step 2: Select the technological process
Enterprises and factories should prioritize the selection of advanced technologies to put into production. The advantages of this are increased productivity, easy operation, precision machining and especially saving a lot of production costs.
- Step 3: Safety measures
Enterprises may consider installing additional backup sources, labor safety measures, fire and explosion prevention measures, lightning columns, ventilation, etc. to ensure the safety of machinery and equipment systems. and workers.
- Step 4: Measures to improve the operational efficiency of the power supply system
Applying methods to help improve power factor, reactive power compensation, reasonable arrangement of capacitors, etc., in order to increase operational efficiency for the power supply system of industrial enterprises.
4.2 Operation phase
Good operation of the industrial electrical system at a machine-manufacturing enterprise can effectively exploit the advantages of the power network. Some of the measures that can be applied during this period are as follows:
- Step 1: Calculate and adjust the load balance in factories and enterprises so that the load graph is relatively flat;
- Step 2: Determine and set the transformer operation at the enterprise in a more optimal way, minimizing the under-load condition on the transformer during the load time in the small enterprises;
- Step 3: Determine and set the appropriate operating mode on machines with large capacity such as: air compressors, furnaces, electric furnaces, large machine tools,…;
- Apply appropriate production measures to limit the situation of machines having to idling during production.
Efficient design and operation of the power supply system of an industrial enterprise will help improve production capacity, as well as minimize unnecessary costs. It can be said that the electrical system is the first key to the efficient operation of a machine-building enterprise.
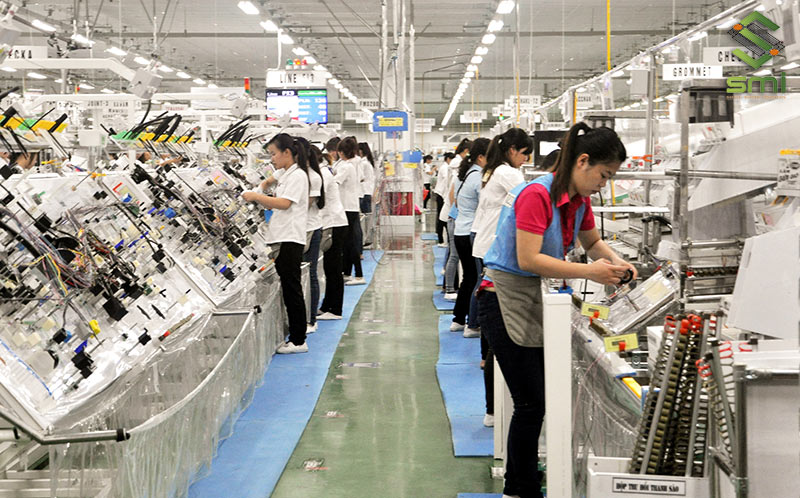

However, effective management of industrial electrical networks is not an easy matter. Most large enterprises now choose professional electrical system design and construction services to save time and ensure compliance with the above standards.
SUMITECH with more than 10 years of experience in the field of design and installation of industrial electrical systems has been a companion of many businesses. Like ABB, Honda Vietnam, Goshi, Toto…
Coming to SUMITECH’s services, customers will experience:
- Fast and professional working process;
- Consulting, designing the most optimal industrial electrical system;
- Show industrial electrical networks in detail and intuitively with professional 3D drawings;
- A team of highly qualified and experienced technical staff brings outstanding quality to the project.
Contact us immediately to get a detailed quote from an engineer for the power supply system of an industrial enterprise.
- Hotline: 024 7108 8838 – 0989060987
